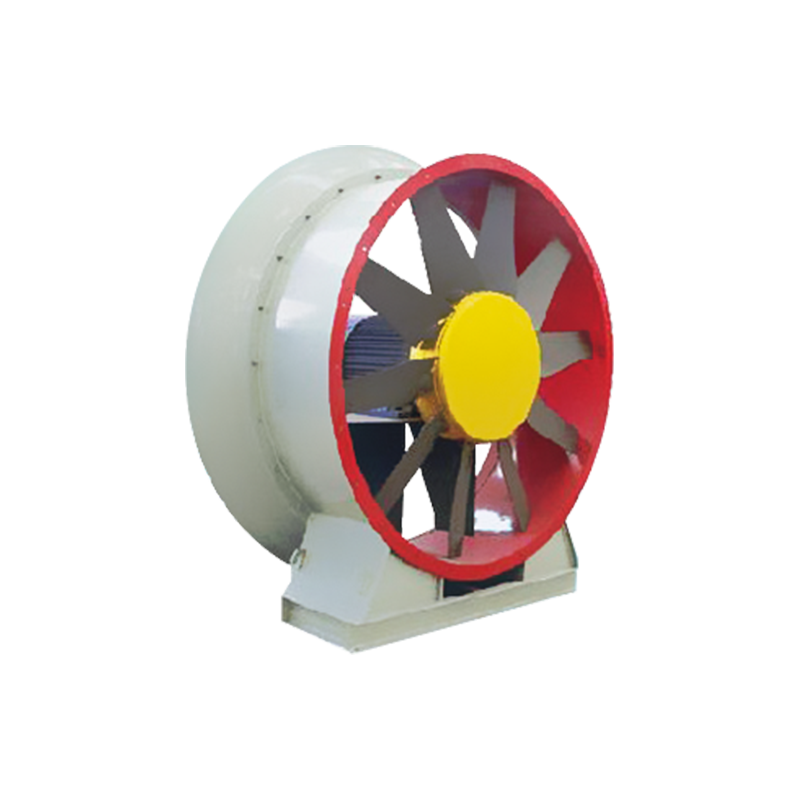
1. Number of blades
The blade number design of the T35 axial flow fan usually follows the general principle of cooling fan design, that is, an odd number of blades. This is because the blades with an even number of blades are easy to be symmetrical in shape and difficult to maintain balance, which may cause the fan to resonate during operation, and then cause the fan blades or bearings to break. The design of an odd number of blades helps to reduce this risk and improve the stability and reliability of the fan. The number of blades is not the more the better. Too many blades will increase the resistance and noise of the fan, while reducing the air volume and air pressure. Therefore, in the design of the T35 axial flow fan, the number of blades needs to be accurately calculated and tested to achieve the best performance effect.
2. Blade spacing
The blade spacing is one of the important factors affecting the performance of the T35 axial flow fan. Appropriate blade spacing helps to maintain the smooth flow of airflow and improve the efficiency and performance of the fan. When the blade spacing is too small, the airflow disturbance will increase, and the friction on the blade surface will also increase accordingly, which may reduce the speed and efficiency of the fan, thereby affecting the output of air volume and air pressure. If the blade pitch is too large, although it can reduce the friction between the blades, it will increase the pressure loss, resulting in insufficient wind pressure and reduced air volume. Appropriate blade pitch helps reduce the noise when the fan is running. Too small blade pitch will increase airflow disturbance, thereby increasing noise; while too large blade pitch may cause unstable vibration and noise when the fan is running. Optimizing the blade pitch can improve the efficiency of the fan. By accurately calculating and adjusting the blade pitch, it is possible to reduce noise and vibration while ensuring sufficient air volume and air pressure, thereby improving the overall efficiency of the fan.
3. Blade inclination
The blade inclination refers to the angle between the fan blade and the fan axis. The size of this angle directly determines the degree of interaction between the blade and the air during rotation, which in turn affects the performance of the T35 Type Axial Flow Fan. When the blade inclination increases, the wind pressure difference between the upper and lower surfaces of the blade also increases accordingly, allowing the fan to generate a larger air volume and air pressure at the same speed. This is particularly important for application scenarios that require higher air volume and air pressure. Too large blade inclination may also cause excessive pressure on the upper surface of the fan, resulting in backflow, thereby reducing the performance of the fan. Therefore, it is necessary to find a balance point during design so that the blade inclination angle can provide sufficient air volume and air pressure while avoiding the occurrence of backflow. The size of the blade inclination angle will also affect the noise level of the T35 Type Axial Flow Fan. Generally speaking, a smaller blade inclination angle can reduce the noise of the fan, because a smaller inclination angle means that the blade has less friction with the air when rotating. However, too small an inclination angle may lead to insufficient air volume and air pressure, so it is necessary to find a balance point between noise and performance.
4. Blade curvature
Blade curvature refers to the degree of curvature of the blade in the radial direction. In the T35 axial flow fan, the size of the blade curvature also has a certain effect on the performance of the fan. Appropriate blade curvature can increase the blade surface area of the fan and improve the heat dissipation effect of the fan. At the same time, a larger blade curvature can also enable the fan to generate greater gas kinetic energy at the same speed, that is, greater air volume and air pressure. However, an excessively large blade curvature will also increase the resistance of the blade and the torque requirement of the motor, reducing the efficiency and reliability of the fan. In the design of the T35 axial flow fan, the blade curvature needs to be reasonably set according to the specific application scenario and performance requirements.
5. Blade smoothness
The smoothness of the blade also has a certain impact on the performance of the T35 axial flow fan. The smooth blade surface can reduce the turbulence and resistance of the airflow on the blade, reduce noise and vibration, and improve the efficiency and stability of the fan. In the design and manufacturing process of the T35 axial flow fan, advanced mold forming and post-processing processes are required to ensure the smoothness and flatness of the blade surface.

 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى